Protect your WordPress website from any threat
Iron Security is the ultimate WordPress security plugin
If you own a WooCommerce store and wish to stay away from security risks, it’s important to understand how to implement a content security policy header. We all know WooCommerce is a popular platform with over 6 million WooCommerce stores around the world; this makes it vulnerable to attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS), data injection, and Magecart-style card skimming.
So, if you understand the content security policy header, it will prevent you from any threats on the internet and help you run your e-commerce store smoothly.
What is a Content Security Policy Header?
Let’s understand the content security policy header. It is an HTTP response header that guides a browser to load essential parts of your website. The web server is responsible for sending this header as part of the HTTP response.
The CSP header is a type of HTTP header used to protect web applications by controlling which resources a web page can load. The policy applies to each web page individually, helping to secure the entire web application. The CSP header plays an important role in blocking malicious and unauthorized code. This security add-on prevents attackers from installing or running scripts or protects customer information at the time of checkout.
CSP can be set using a meta tag, which is a useful option for static resources or when server headers cannot be modified. CSP should ideally be set on all responses to all requests, not just the main document.
Why Your WooCommerce Store Needs a Content Security Policy Header?
How to Implement Content Security Policy Header in WooCommerce
Method 1: Using a Plugin
If you have no technical idea, you can use plugins to configure your Content Security Policy header without coding.
For this we are going to utilize Iron Security Plugin which is from WPIron. If you can follow these simple steps to get started.
- First, log in to your WordPress website.
- From the WordPress Dashboard, navigate to Plugin >> Add Plugin.
- Now activate the plugin, and from the left of the dashboard click on “Iron Security.”
- After this, click on the “HTTP Security & Headers” option from the options.
-
Finally, you can simply enable the “Content Security Policy Headers” by toggling them on.
Method 2: Using .htaccess (Apache Servers) and functions.php (WordPress Theme)
.htaccess (Apache Servers)
The web server is responsible for sending the Content Security Policy (CSP) header as part of the HTTP response to enforce security rules in browsers.
Here is a code that you should add in the .htaccess file. This file is inside the root directory inside WordPress:
< IfModule mod_headers.c>
Header set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://js.stripe.com https://www.googletagmanager.com; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://fonts.googleapis.com; img-src 'self' data: https://*.gravatar.com; font-src 'self' https://fonts.googleapis.com; connect-src 'self' https://api.stripe.com; frame-ancestors 'none';"
< /IfModule>The default-src directive in the code above sets the default policy for loading resources and is known as the default src directive. The script src directive (script-src) controls which scripts can be loaded, while other directives like object-src, frame-src, and media-src specify allowed sources for plugins, frames, and media files, respectively.
Fetch directives such as connect-src and img-src determine how the browser can load resources from different origins. Using ‘self’ in these directives enforces a same origin policy, which helps prevent unauthorized access and enhances web security by ensuring resources are only loaded from trusted sources. This approach helps the web server securely load resources and protect against threats like cross-site scripting (XSS).
functions.php (WordPress Theme)
Locate your functions.php file of your theme file and paste this:
function add_csp_header() {
if (!is_admin()) {
$csp = "default-src 'self'; " .
"script-src 'self' 'nonce-" . wp_create_nonce('csp') . "' https://js.stripe.com https://www.googletagmanager.com; " .
"style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://fonts.googleapis.com; " .
"img-src 'self' data: https://*.gravatar.com; " .
"font-src 'self' https://fonts.googleapis.com; " .
"connect-src 'self' https://api.stripe.com; " .
"frame-ancestors 'none'; " .
"report-uri /csp-violation-report-endpoint";
header("Content-Security-Policy: " . $csp);
}
}
add_action('send_headers', 'add_csp_header', 100);
The nonce attribute is used in Content Security Policy (CSP) directives to allow specific inline scripts and inline styles to execute securely. For each HTTP response, a random value is generated and set as the nonce attribute on your script elements and style tags. This approach enables you to execute inline script and inline styles while blocking unauthorized inline code, such as inline event handlers or other unsafe inline JavaScript code.
To enhance security, always avoid unsafe inline and do not use the unsafe-eval directive, as it allows potentially dangerous JavaScript code execution. Each content security policy directive, like script-src or style-src, can be customized using the following directive syntax to control which script elements and JavaScript code are permitted to run.
How to add HTTP Security & Content Security Headers using Iron Security?
Iron Security is a free-to-use security plugin that has essential features for your website protection. If you are not familiar with coding and want to easily implement security features, you can use this plugin. This website is compatible with platforms like WooCommerce and WordPress with support for favorite WordPress themes such as Astra, Divi, and so on.
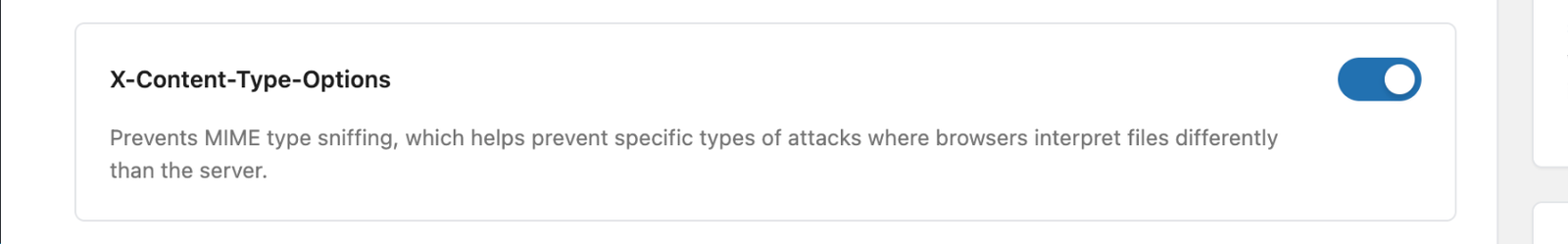
X-Content-Type-Options Prevents MIME type sniffing
It prevents browsers from sniffing MIME types, which helps stop some attacks where browsers read files differently than the server.
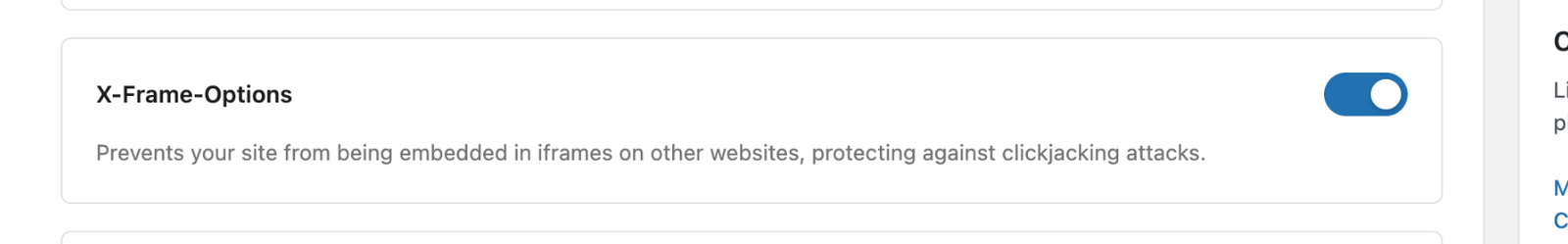
X-Frame-Options Prevents clickjacking attacks
It prevents other websites from putting your site in iframes, thereby protecting you from clickjacking attacks.
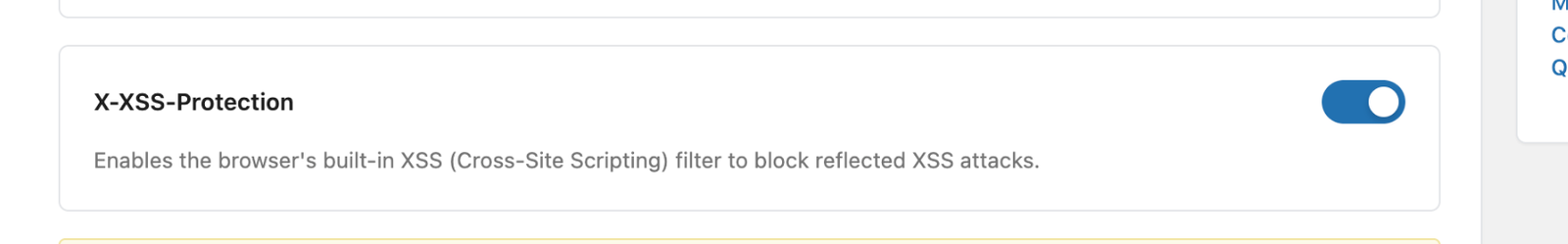
X-XSS-Protection Blocks reflected XSS attacks
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks can’t happen if the browser’s built-in XSS filter is turned on.
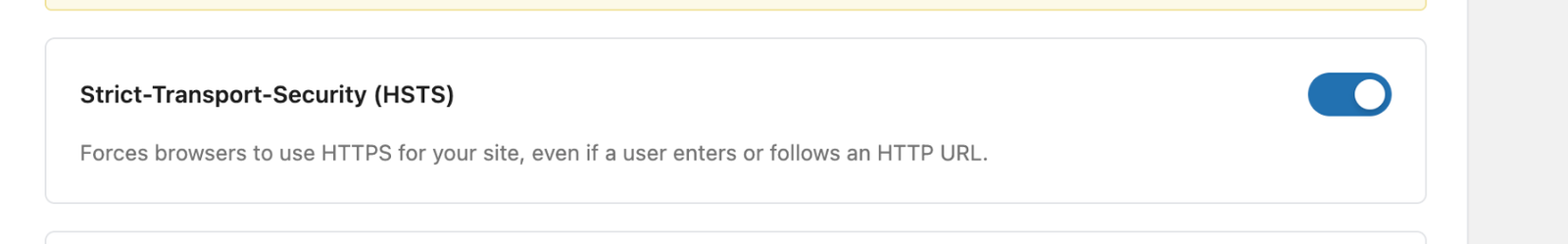
Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS)
You can make browsers use HTTPS for your site even if they enter or follow an HTTP URL.
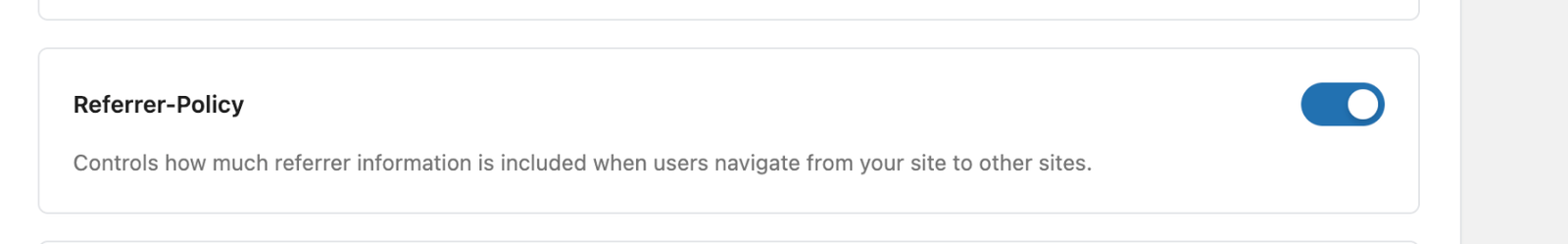
Referrer-Policy
Sets how much information about the site that sent the user to yours is sent back to your site.
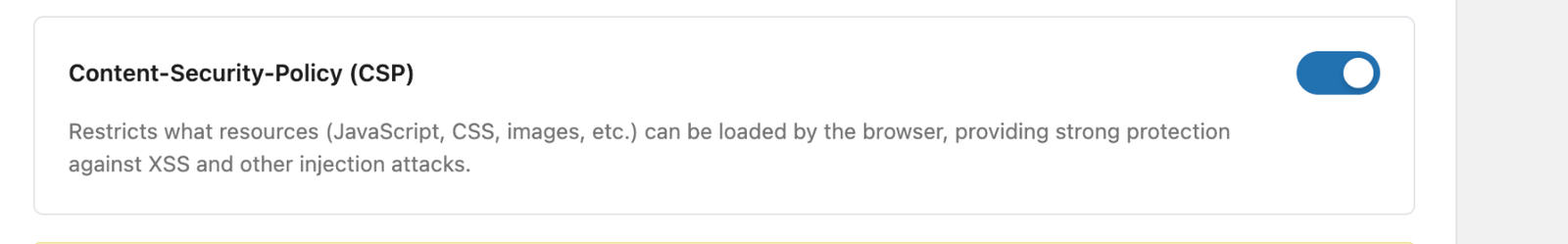
Content Security Policy Headers
Limits the resources (JavaScript, CSS, images, etc.) that the browser can load. Content security policies (CSPs) use various csp directives to control how a requested resource is loaded and what permissions it has.
These policies can apply to a requested resource similar to how the iframe sandbox attribute works, restricting the capabilities of embedded content. CSP can also control resources loaded in nested browsing contexts, such as iframes, and the ‘child-src’ directive can be used to specify which sources are allowed for nested browsing contexts loaded within the page. This protects against XSS and other injection attacks very well.
Permissions-Policy
It tells your site and embedded content which browser features and APIs (like the camera, microphone, and geolocation) can be used.
Maintaining Your Content Security Policy Header
Regular Security Audits
It’s important to review your Content Security Policy header every three months. This ensures your website keeps up with WooCommerce’s future updates and protects your website from new security threats.
Monitor Industry Updates
As a WooCommerce site owner, stay updated with the different CSP directives and updated browsers.
- W3C CSP specification updates
- Mozilla Developer Network
- WooCommerce security advisories
Performance Impact Assessment
You shouldn’t stop after implementing the security header. Actively monitor your website performance and keep an eye on your security measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we hope you could understand the importance of strong Content Security Policy headers. As a successful business, it becomes your responsibility to protect your customers from internet threats and data breaches. In addition to this, you should implement other practices, like adding SSL certificates, to make your website more secure.
Your customers prefer to be loyal to your business only if they feel secure about their information. Therefore, it’s crucial to give your time and money to perfectly set up the CSP header in your WooCommerce store.
Protect your WordPress website from any threat
Iron Security is the ultimate WordPress security plugin
Frequently Asked Questions
Can CSP prevent all security threats?
No, CSP headers are one of many security measures for your website. If you wish to utilize full security support, start using SSL, update regularly, choose secure hosting, and also utilize Web Application Firewalls (WAF).
What is a content security policy header?
Content Security Policy The header, in other words, is known as the HTTP response header. It is a rule that directs a web browser to load safe and selected resources to load from your website.
How does a content security policy header protect my WooCommerce store?
It acts as a protection layer that restricts unauthorized resources. There are different threats that are blocked by CSP headers, like XSS attacks, data injection, clickjacking, Magecart-style attacks, and so on.
Is implementing a CSP header required for PCI compliance?
Yes, PCI compliance, also known as PCI DSS 4.0 Requirement 6.4.3, is the rule that directs all the website owners to safeguard the data and information of the customers from being stolen.
Will a CSP header break my WooCommerce functionality?
There are very rare chances that a CSP header could break your WooCommerce functionality. CSP can be tested in report-only mode to view violations without blocking content. This helps you to find problems in your ecommerce store.
How long does it take to implement a CSP header?
It may take approximately 2 days to fully implement the CSP header, but remember that testing for bugs and making your system bug-free may take several days.
What should I do if my CSP blocks legitimate resources?
You can view violation reports to determine if any legitimate resources are blocked. After this, you can modify your policies to enable them. Before you start doing this, it is recommended to make changes in a staging website.
How often should I update my content security policy header?
It is recommended to update your content security policy header every three months and also always during the time you decide to add updated features, new plugins, or a different mode of payment.
Does CSP work with all browsers?
Yes, all the new browsers support the Content Resource Policy header. For old browsers, they won’t accept the security header that prevents the compatibility risks. CSP is supported by all major modern browsers, but is not supported in Internet Explorer. Internet Explorer does not fully support modern Content Security Policy features and may require legacy headers or alternative security measures.